The Ethereum Pectra upgrade is the next major improvement to the Ethereum network, expected in Q1 2025. This upgrade may include features such as increasing the maximum stake for validators, improving the performance of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), and improving the user experience for wallets.
What is the Ethereum Pectra upgrade?
Ethereum developers are looking forward to the next major upgrade, Pectra, following the success of the Decun upgrade. The main goal of Pectra is to improve wallet functionality to provide a better user experience.
Imagine accessing your wallet the same way you log into your social media account. Even if you forget your password, you can still recover your assets without risking loss.
With the Pectra upgrade, accessing and managing Ethereum wallets like MetaMask will become simpler. This update will also slow down validator entry to protect the system from overload.
In this article, let’s explore the Pectra upgrade and three major Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs): EIP-3074, EIP-7702, and EIP-7251.
Understanding the Prague/Electra Upgrade
The Prague and Electra upgrades have been merged to form Pectra. Following Ethereum’s traditional naming convention, the execution and consensus layer upgrades are often named after stars and cities.
This update is expected to be released sometime between Q4 2024 and Q1 2025. After this update, Ethereum aims to strengthen its ecosystem by improving the efficiency, security, and scalability of the network.
The Pectra upgrade plays a pivotal role in the development of Ethereum, with active participation from the developer community to improve the network’s capabilities. This update is expected to introduce several Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), of which EIP-3074 and EIP-7251 are the most notable, with EIP-7702 to follow.
What is EIP-3074?
EIP-3074 enhances the functionality of Ethereum by reducing the difficulty of managing traditional wallets like Trust Wallet. Traditional wallets, known as externally owned accounts (EOAs), will be integrated with smart contracts through account abstraction, providing a smoother user experience.
For example, in a typical process, to buy your favorite NFT, you need to sign two transactions: one to allow the marketplace to debit the amount from the wallet and one to complete the payment. With EIP-3074, smart contracts in your wallet will operate according to the ERC-4337 standard, ensuring that both transactions are executed with a single signature.
Additionally, digital signatures allow you to access and manage your wallet without storing your private keys. For this reason, even if you lose your password and recovery phrase, you still have the option to recover them to protect your assets.
How does EIP-3074 work?
EIP-3074 adds two new EVM commands: AUTH and AUTHCALL.
AUTH: Sets an authorized context variable with an ECDSA signature, temporarily representing the functions of the EOA.
AUTHCALL: Allows smart contracts to perform operations on behalf of the EOA, similar to how the wallet owner performs a call.
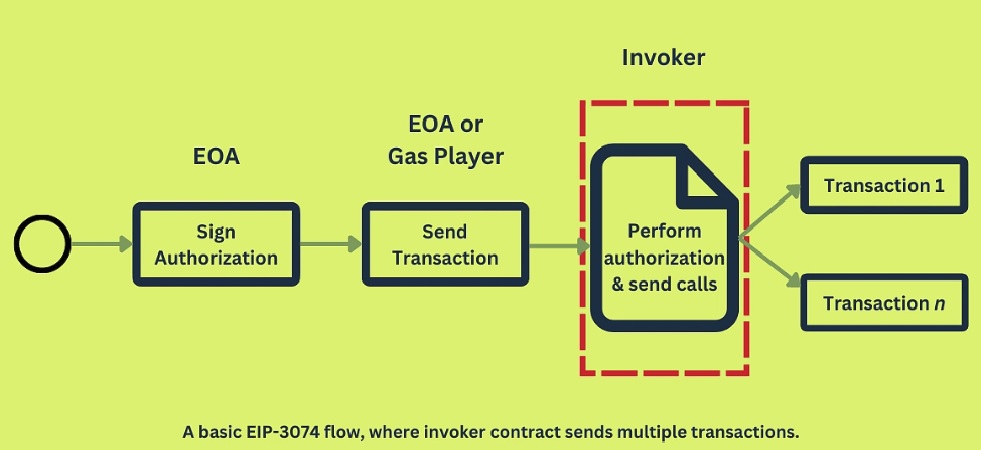
Implementing these EVM commands allows smart contracts to authorize and execute transactions from EOA with a single signature, saving users time, effort, and gas fees.
Basic EIP-3074 Flow
For example, before EIP-3074, you needed to sign and submit each operation to interact with a dApp, such as swapping or staking tokens. With EIP-3074, you only need to sign one authorization command; the AUTH and AUTHCALL commands will automatically perform all the remaining functions.
Advantages of EIP-3074
Key advantages of this Ethereum improvement proposal
- Social recovery mechanism
Losing the private key in an EOA wallet means losing all assets, which is a concern for new Web3 users. With EIP-3074, invoker contracts are configured to recover assets through social recovery, allowing you to recover your wallet even if you lose your private keys.
Enhanced transaction workflow: EIP-3074 enables multiple transactions to be executed simultaneously through smart contracts with a single signature, saving time, effort, and gas fees.
- Improved user experience
EIP-3074 facilitates the deployment of automated DeFi strategies, eliminating the need for users to constantly monitor the market. Cross-chain asset transfers are also simplified, allowing users to manage assets across multiple chains with a single signature.
- Sponsored transactions
EIP-3074 allows third parties to pay gas fees for users’ transactions, allowing them to interact with dApps without managing gas fees, thereby attracting new users.
What is EIP-7702?
Vitalik Buterin wrote EIP-7702 just 22 minutes before the Ethereum Foundation (EF) meeting to discuss EIP-3074. Jarrod Watts, developer relations engineer at Polygon, mentioned on X that this new proposal will have a big impact on Ethereum.
EIP-7702, which was just introduced, is a more advanced version of EIP-3074, while also being more compatible with account abstraction (ERC-4337). It acts as a compromise between ERC-4337 and EIP-3074.
With EIP-7702, externally owned accounts (EOAs) will act as smart contract wallets for a short time while making transactions, and will return to their original state after completion.
Key Differences Between EIP-3074 and EIP-7702
| EIP-3074 | EIP-7702 |
|---|---|
| Introducing the two opcodes AUTH and AUTHCALL | Introducing a new transaction type called user_operation |
| Not compatible with future account abstraction | Compatible with future AA implementations |
| Assign EOA control to smart contract code | Smart contract code added to EOA address |
EIP-3074 Risk Assessment
The innovation of EIP-3074, which allows smart contracts to connect to traditional EOA wallets, brings many improved features to the Ethereum ecosystem. However, the addition of new functionality can also lead to security vulnerabilities.
A major risk associated with EIP-3074 is the potential for misuse of invoker contracts. Insecure implementations can create opportunities for bad actors to exploit this vulnerability to steal assets or perform unauthorized transactions.
It is important to ensure that EIP-3074-based transactions are executed with trusted invoker contracts. Developers should implement security measures, such as whitelisting, to limit the participation of unsafe entities.
Additionally, projects can conduct regular audits with reputable smart contract auditing firms such as Hacken or Slowmist to detect and fix security risks.
Finally, educating users on security procedures is essential to raise awareness and protect their assets, helping wallet owners spot warning signs and avoid loss of crypto assets.
What is EIP-7251?
EIP-7251 is an important Ethereum improvement proposal to address the increase in the number of validators on the network. As of April 2024, the number of validators has surpassed one million, with over 32 million ETH staked.
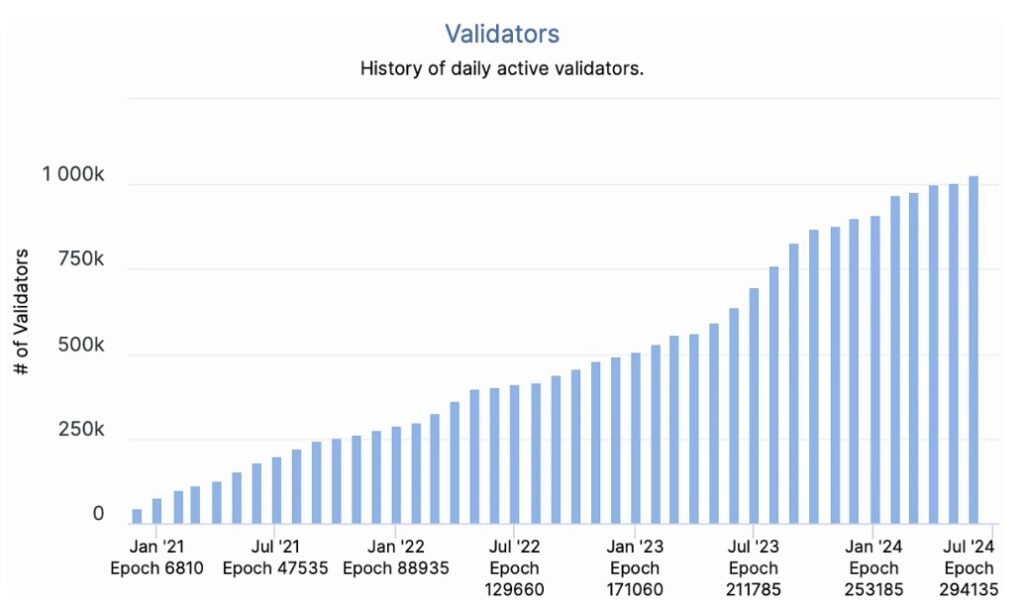
This proposal increases the maximum effective balance (MaxEB) of a validator from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH, while keeping the minimum balance at 32 ETH. EIP-7251 is designed to encourage large staking service providers such as Binance to support the integration of a large number of validators, thereby reducing the load on the network without affecting economic security.
How does EIP-7251 work?
EIP-7251 operates based on two main streams: the voluntary exit stream and the validator merge stream.
Voluntary exit stream
The validator transmits the VoluntaryExit object after signing it over the P2P network to integrate it into the Beacon block. Next, the initiate_validator_exit function is called during Beacon block processing, assigning the withdrawable_epoch and exit_epoch values to the current validator in the Beacon State.
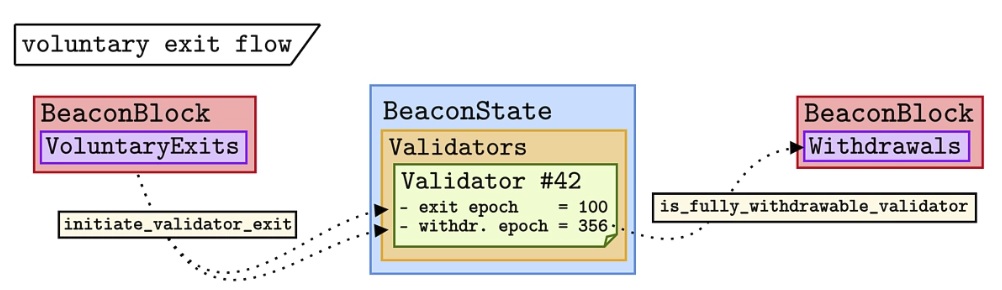
The validator will then perform the consensus task and leave the exit queue after a waiting period. Exit_epoch defines the delay when the validator is no longer active and stops performing tasks in the Beacon Chain.
Validators can only withdraw staked ETH after reaching the withdrawable stage, which includes a delay of approximately 27 hours. This timeout is designed to detect protocol violations by validators and apply penalties to violations before allowing them to exit ETH.
Validator Consolidation Flow
EIP-7251 also modifies the mechanism that allows validator consolidation by triggering VoluntaryExit during Beacon block processing. Voluntary exit of validators is triggered during Beacon block processing using the initiate_validator_exit function.
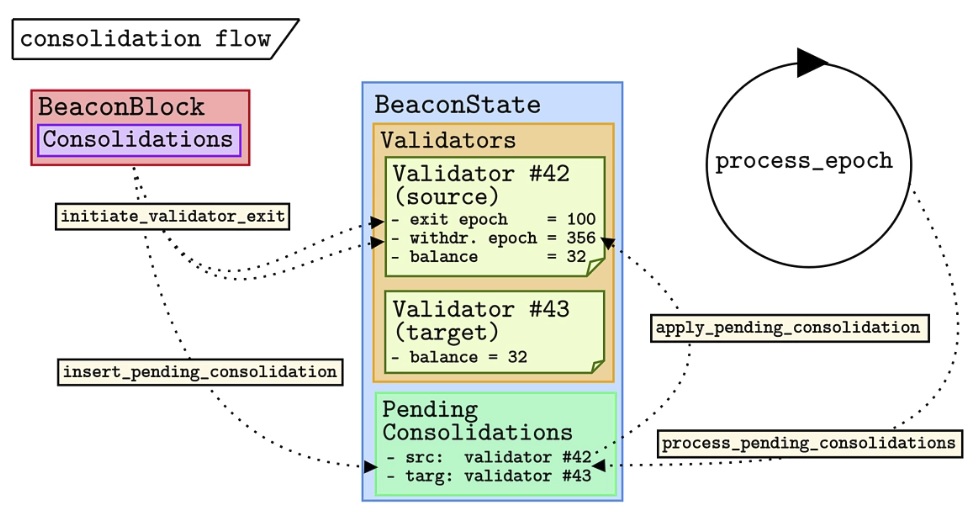
Functions such as insert_pending_consolidation and apply_pending_consolidation will be called to complete the consolidation process, transferring balances from the source validator to the target validator.
EIP-7251 Features
- Solves the Challenge of the Consensus Layer
Proposed to reduce withdrawals from the increased MaxEB, supporting the expansion of the Ethereum ecosystem.
- Reduced Overhead
Reducing the number of validators will result in reduced operating costs, allowing savings to be used for other useful purposes.
Benefits for Solo Stakers
While large staking providers are the main beneficiaries, solo stakers can also take advantage of the opportunity to pool rewards when staking smaller amounts of ETH.
EIP-7251 Risk Mitigation
The biggest concern with EIP-7251 is the risk of slashing. This mechanism will penalize offending validators, requiring them to stake at least 32 ETH to avoid the risk of losing ETH. The initial penalty is 1 ETH or 1/32 of the total staked ETH. However, new proposals could change the penalty rate to 1/4,096 staked ETH.
Other Important EIPs Proposed
Over 25 EIPs have been proposed for the Pectra upgrade, with notable proposals including:
- EIP-2537
This proposal aims to improve the integration of operations on the BLS12-381 curve, allowing for complex operations in cryptography, thereby improving the efficiency of multi-party computation (MPC) protocols.
- EIP-2935
To support stateless execution, this proposal stores the last 8,192 historical block hashes in the system contract memory, integrated into the block processing logic.
- EIP-6110
This proposal allows for validation deposits to be added to the execution block as a list of deposit operations, to optimize processing.
- EIP-7002
This proposal allows validators to use withdrawal credentials at the execution layer to perform partial withdrawals and trigger an exit mechanism in the Ethereum Proof of Stake (PoS) system.
- EIP-7549
The committee index field has been moved outside of the signed Attestation message, allowing for efficient aggregation of consensus votes.
- EIP-7685
This proposal creates a general-purpose framework that stores contract activation requests and displays requests from the consensus layer.
Conclusion
The Pectra upgrade marks a major step forward for Ethereum with improvements ranging from security to user experience. The focus on smart contract capabilities for regular wallets and improving maximum effective balances for validators represent a significant development. However, the mix of excitement and anxiety from the community about these changes should be kept in mind, especially the potential risks associated with staking limits and social resilience tools.

