When you first hear about Bitcoin staking, you may feel confused, as Bitcoin operates on a Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism. However, Bitcoin staking is an ongoing reality, with thousands of addresses participating to optimize the returns on their assets. Here are the important information you need to know.
What is Bitcoin Staking?
Staking typically involves holders locking up digital assets to participate in network activities, such as confirming transactions on Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchains. Although Bitcoin does not support direct staking due to its PoW mechanism, the emergence of platforms offering Bitcoin-based Liquid Staking tokens (LST) has opened up the possibility of participating in indirect staking.
EigenLayer, Babylon, and AVS
On the Ethereum network, the concept of Restaking was introduced in 2023 with EigenLayer and gained significant traction in mid-2024, with a total value locked exceeding $20 billion. ETH staking helps secure the Ethereum network and rewards participants. EigenLayer allows users to reuse their ETH stake to secure additional services and earn additional rewards.
Originally called Active Validated Services (AVS) on EigenLayer, these applications are now expanding to the Bitcoin blockchain, with Babylon leading the way in building an architecture that allows applications to leverage Bitcoin’s economic security. On Ethereum, protocols like Symbiotic and EigenLayer also accept tokens like Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) to enhance the security of applications.
Understanding Bitcoin Staking
In Bitcoin staking, users deposit BTC into the protocol and receive Liquid Staking tokens in return, representing the BTC staked. These Liquid Staking tokens typically provide greater liquidity and other functions, allowing participants to participate in DeFi without giving up staking rewards.
The most popular Bitcoin Liquid Staking today is LBTC, issued by the Lombard protocol.
How LBTC is created: Users deposit BTC to special addresses associated with the Babylon protocol, thereby creating LBTC on Ethereum, which acts as a representation of the Bitcoin sent.
Where the BTC goes: The actual BTC is held in Babylon protocol contracts, which are kept safe but not used during this time.
Rewards for the sender: During the time the BTC is held, the sender receives rewards from both Babylon and Lombard to incentivize participation.
Future Plans: The goal is to use BTC in Babylon contracts to secure a larger ecosystem, allowing other applications and chains to use BTC for added security.
Top Protocols in Bitcoin Staking
Some of the prominent protocols in the Bitcoin staking space include:
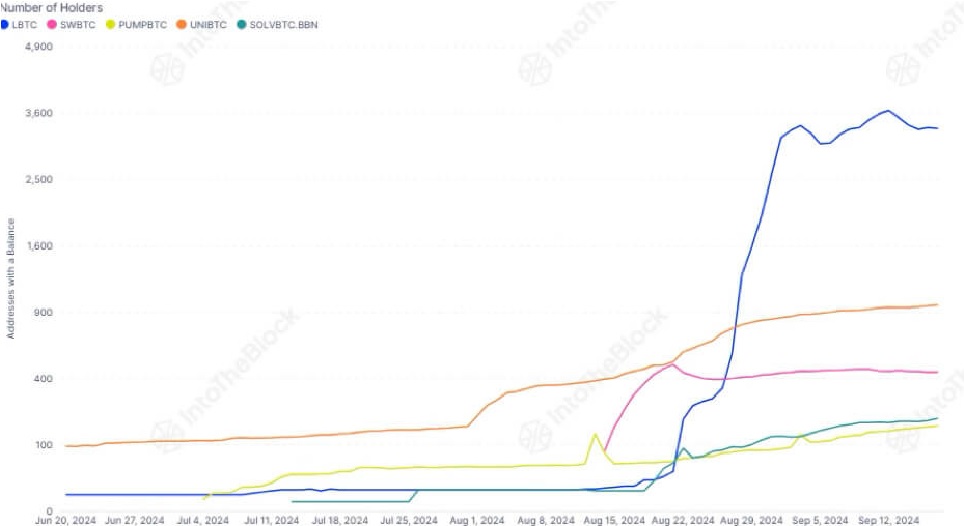
Lombard Staked BTC (LBTC): Dominating the market with a $300 million market cap and over 3,000 holders.
UniBTC: Gained a significant number of holders early on, currently around 1,000.
Swell BTC (SWBTC): Started strong but has slowed down, currently ranked third with around 440 holders.
Is Bitcoin Staking the Future of Bitcoin Yields?
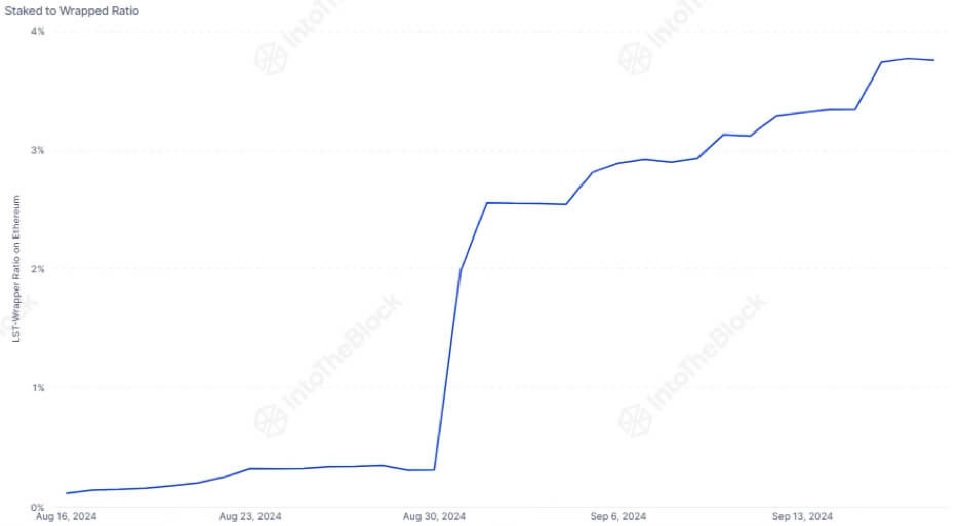
Bitcoin Staking has had a strong start with thousands of holders participating. Currently, Bitcoin staked accounts for 3.75% of all Wrapped Bitcoin, indicating potential for future growth.
The concept is promising, but long-term success will depend on the sustainability of the staking economics beyond the initial rewards. The development of services built on these protocols will determine whether Bitcoin staking can become one of the most attractive profit opportunities for Bitcoin holders.

